For calculation of tax, we need to have tax base amount and tax rate.
Tax rate is the tax percentage which is to be applied on tax base amount to arrive at tax amount. Tax base amount is the amount on which tax rate is to be applied.
As directed by tax authority in a country:
Every country has a list of different taxes which may be applicable on a business transaction in the country.
Different business transaction might invite different types of taxes with different tax rates.
Tax base amount can be inclusive or exclusive of cash discount.
Once tax base amount and tax rate is known for a transaction, tax amount can be calculated.
Calculated tax amount along with business transaction details need to be recorded.
Let’s see how sap handles the above requirements for tax calculation
Every country has a list of different taxes which may be applicable on a business transaction in the country.
TAX PROCEDURE
In sap, country specific tax procedure is created and assigned to country. Tax procedure is a list of tax condition types. Each condition type represents a type of tax applicable in the country.
Hence tax procedure represents the list of different types of taxes which are valid in the country.
TAX CODE, TAX JURISDICTION CODE
Different business transaction might invite different types of taxes with different tax rates.
In sap, tax code is created to store the value of tax percentage.
A business transaction might invite different type of taxes with different tax rates. Hence in sap, tax condition types are assigned to tax percentage. This combination of tax condition types and corresponding tax percentage is stored in tax code.
A tax code in sap is a two digit alphanumeric code which stores different tax conditions (defined in tax procedure) and corresponding tax percentage.
Normally tax code is created at national level but in few countries like USA, different areas have different tax authority and each tax authority decides its own tax percentage. Hence applicable tax percentage depends upon which tax authority the business transaction belongs to.
In sap, each tax authority is created as tax jurisdiction code.
Hence in USA, tax percentages are assigned to tax condition types for the combination of tax code and tax jurisdiction code.
When a business transaction happens, tax code is supplied and system derives tax jurisdiction code information. Corresponding tax percentage maintained against tax condition type is applied for tax amount calculation. Tax amount is posted to GL account assigned to condition type.
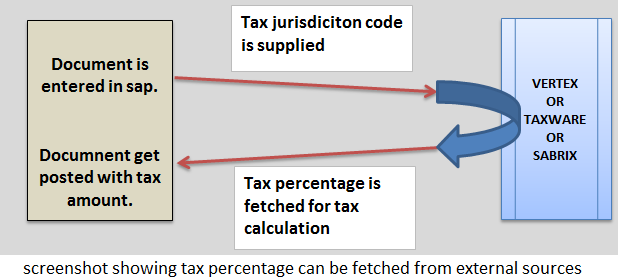
With huge number of tax jurisdiction code (tax authority) and each are regulating its own tax percentage, it becomes very challenging for companies to keep track to up to date tax percentage. Instead of committing resources on keeping track of tax percentage, companies take help from other companies who maintain up to date tax percentage for each tax jurisdiction code.
Companies like vertex, taxware, sabrix maintain tax percentage on their server. When transaction is entered in sap, software determines the jurisdiction code and fetches tax percentage from vertex/ taxware/ sabrix server.
Hence companies free themselves from the load of maintaining tax percentages by using the services provided by other companies. Hence tax percentage is fetched from external sources like vertex, sabrix and taxware.
TAX BASE AMOUNT
Tax base amount can be inclusive or exclusive of cash discount.
In sap, for each company code we can define if tax base amount is inclusive of cash discount or exclusive of tax discount.
POSTING OF TAX AMOUNT
When a business transaction is recorded, tax code is supplied. System calculates the tax amount for each condition type. Condition types are mapped to account key and account key is linked to GL account.
When document is posted, system automatically picks the mapped GL account for posting tax amount.
Let’s put the entire concept together to understand calculation and posting of tax amount in sap
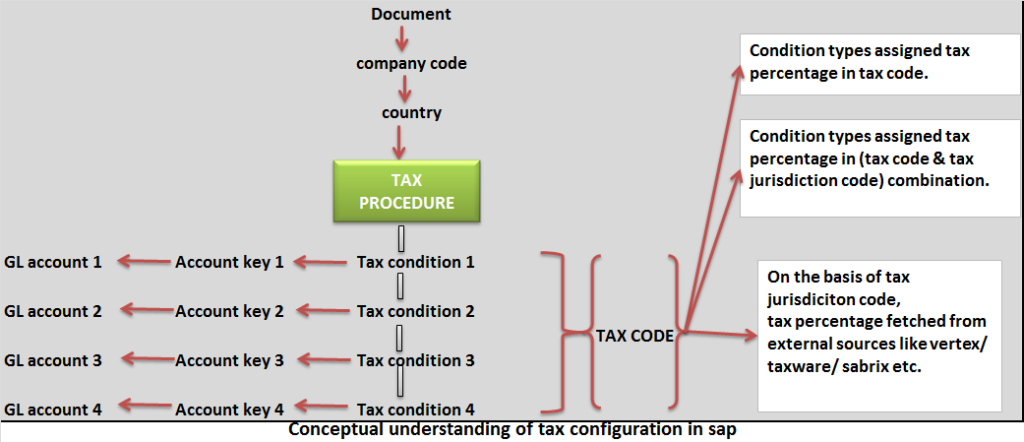
From entered document, system knows the company code. Company code leads to country and country leads to tax procedure.
From tax code which is entered while posting document, system fetches the percentage against each tax condition type and applies the percentage on determined tax base amount.
— Tax condition types are assigned tax percentage in tax code.
— Tax condition types are assigned tax percentage in (tax code and tax jurisdiction code) combination.
— Tax percentage is fetched from external sources like vertex/ taxware/ sabrix etc on the basis of tax jurisdiction code.
Calculated tax is posted in GL account assigned to tax condition type.
GL ACCOUNTING
- What is SAP FICO ?What business requirement is fulfilled in this module?
- What is enterprise structure in sap fico?
- What is GL account? What is account group? What is operational chart of accounts?
- What is the need of country chart of account or alternate chart of account? How country chart of account helps fulfill a business requirement?
- What is the need for group chart of account? How group chart of account helps in consolidation of financial data?
- What is non leading ledger in sap fico?
- What is company code global settings? What global parameter is assigned to company code?
- What is fiscal year variant? Why fiscal year variant is assigned to company code?
- What is posting period variant? Why posting period variant is assigned to company code?
- What is field status variant? What is field status group?
- What is document type in sap? Explain the purpose of document type?
- Document date vs Posting date vs Entry date vs Translation date. Explain
- What is posting key? what is the use of posting key?
- Document header & line items capture information of business transaction.
- Everything about currency & exchange rate in sap.
- Foreign currency valuation in sap. Explain with example
- Retained earnings account helps in year end balance carry forward. Explain
- What is the significance of tolerance groups in sap?
- What parameters are maintained in GL master and how does it impact in document posting?
ACCOUNTS PAYABLE
- What is meant by accounts payable in sap?
- Understanding procure to pay (PTP) cycle and accounting document at each step.
- Understanding MM FI integration in very simple terms.
- Purchase order price determination in SAP. Explained in very simple words.
- House bank, Bank key, Account ID in SAP
- What configuration (FBZP) needed for executing F110 in sap ?
ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE
- How sap overcomes challenges in accounts receivable process?
- What is customer reconciliation account?
- Understanding order to cash cycle in sap.
- Understanding SD FI integration in very simple terms.
- What is lock box? How lockbox helps in collection from customers?
TAX ACCOUNTING
- How sap helps in tax accounting?
- Tax configuration in sap: Tax procedure, Tax code & Tax jurisdiction code
- Concept of tax jurisdiction code & tax jurisdiction structure
- Significance of “Tax category & Posting without tax allowed” in GL master.
- Tax base amount and Discount base amount
- Assigning tax code V0 & A0 for non taxable transaction?
- Deductible input tax vs non deductible input tax
WITHHOLDING TAX
- Withholding tax in sap explained with example.
- How sap overcomes challenges in managing withholding tax?
- Withholding at the time of invoice or payment
- Withholding tax configuration in sap
- Business place & Section code in sap
- Withholding tax certificate numbering in sap
- Withholding tax report for filling tax returns
ASSET ACCOUNTING
- How sap helps in asset accounting?
- What is meant by asset accounting?
- What is the use of asset class?
- What is the use of depreciation key in asset accounting?
- Depreciation area and Chart of depreciation in sap.
- Derived depreciation area VS real depreciation area?
- Understanding asset accounting configuration needed in sap
- GL account determination for posting asset transaction
- Asset transaction and corresponding accounting document?
- How depreciation is posted in sap?
SAP CONTROLLING