Automatic generation of accounting document due to sales activity is referred as SD FI integration.
Below article will help you understand SD FI integration in Order To Cash cycle (sales cycle).
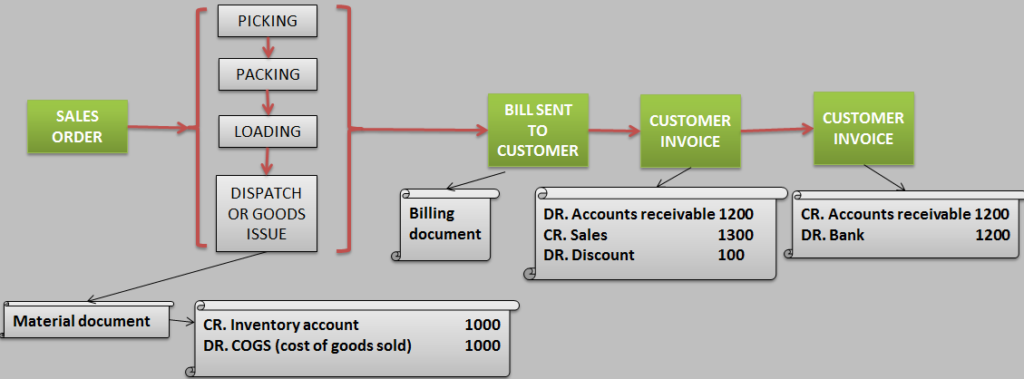
Lets understand accounting document generation at the time of goods issue/ dispatch.
When goods are dispatched, finance document as shown below is posted automatically. Question is how system determines the GL account and amount to post the accounting document?

Since goods are moved hence material document is created. Corresponding finance document gets created as a result of MM-FI integration. GL account for inventory account is picked from OBYC setting (transaction key BSX). GL account for COGS is picked from OBYC setting (transaction key GBB and account modifier VAX).
Inventory & COGS is always valued at standard cost of the material.
Amount calculated = Quantity * standard cost of material per unit.
Let's understand accounting document generation when billing document is released to accounting.
When billing document is released to accounting, accounting document gets posted automatically. Question is how system determines GL account and amount to post accounting document?
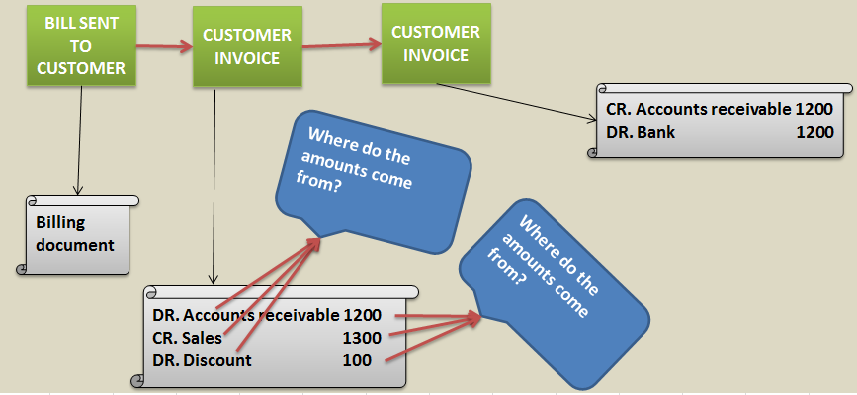
Let’s understand how SD-FI integration enables GL account and amount determination for posting accounting entry.
SD FI integration in detail
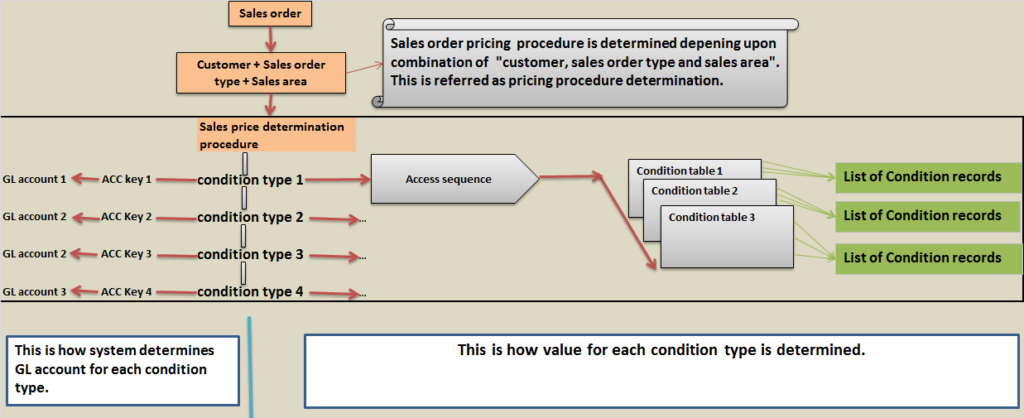
Price determination procedure or pricing procedure
Price determination procedure is basically combination of multiple condition type. Condition type represents different prices that are put together (addition or subtraction) to arrive at net sales price.
Net price = Base price –Discount + surcharge + tax
Each of these prices “Base price, Discount, Surcharge, Tax etc. is created as condition type in sap.
Once pricing procedure is selected, list of all condition types involved is known. Now for each condition type system has to determine the condition value.
Each condition type is linked to an access sequence. Access sequence is basically sequence in which condition tables are to be accessed to search for condition record (Condition records are maintained in condition table).
As per sequence maintained in access sequence, system starts with table 1. If condition record is found then system picks the condition value and stops searching any further. If condition record is not found in table 1 then system starts searching for table 2. If condition record is found then system picks the condition value and stops searching any further, if not found in table 2 then system starts searching in table 3.
If no condition record is found in all the tables, system issues message no record found. Condition type gets zero value.
Similarly value for each & every condition type is determined. System calculates (addition & subtraction of condition values) to arrive at net sales price. This net price is basically the price which is charged to customer. Hence GL account for account receivable is debited with this net price.
Note: Condition types can be real or statistical. Only real condition types are included in price calculation. Statistical condition types are not included in price calculation and are only for information/ reporting purpose.
GL account determination for each condition type:
Till now system has calculated condition type value but GL account needs to be determined for posting accounting entry.
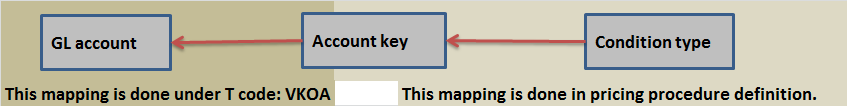
Now business might require to record sales price & discount separately. This can be done by assigning condition type to account key and mapping account key to GL account.
Sap provides large number of predefined account keys. Below are just two examples of account key
ERL – Sales
ERS – Sales deduction or sales discount
All those condition types whose value needs to be posted to sales account are assigned account key ERL
All those condition types whose value needs to be posted to discount account are assigned account key ERS.
We understood how pricing procedure works. How system determines the GL account and amount for posting accounting entry. Now let’s understand how pricing procedure is selected.
Pricing procedure selection process:
Selection of pricing procedure plays a big role in calculation of sale price.
In practical business scenario, sale price depends upon:
Customer:
Company offers different prices to different customers depending upon the kind of business relation that the customer has with company. Hence company categorizes the customers into different categories and customers in a particular category can be offered special discount.
Hence customer play role in selection of pricing procedure.
Distribution channel + Division + Sales organization
Price for online order might be different from showroom price. Wholesale order might be eligible for additional wholesale discount. (Hence distribution channel play role in selection of pricing procedure.)
If you are buying car, price may be composed of base price, insurance charge, road tax etc. But if you are buying bicycle, price may not have insurance charge & road tax. Goods which are being sold play role in selection of pricing procedure. (Hence division play role in selection of pricing procedure)
If you purchase product directly from company or if your purchase from marketing agency (selling on behalf of company), price may differ. (Hence sales organization play role in selection of pricing procedure).
Above examples are given just to help you understand that selection of pricing procedure depends upon combination of Sales organization + Distribution channel + Division
Order type:
Different business scenarios (sales order, return sales order, free samples, rework order etc.) will have different nature of prices involved. Price components involved in sales order can be different from price component involved in return sales order.
Hence, order type play role in selection of pricing procedure.
Overall, selection of pricing procedure depends upon combination of
Order type + Customer + Sales area (sales organization + distribution channel + division)
When a sales order is created, sales order has all information (order type, customer, sales area) necessary for selection of pricing procedure.
From pricing procedure system determines GL account & amount for accounting entry. When billing document (sales document) is released then accounting document (finance document) gets generated automatically. This is referred as SD FI integration.
GL ACCOUNTING
- What is SAP FICO ?What business requirement is fulfilled in this module?
- What is enterprise structure in sap fico?
- What is GL account? What is account group? What is operational chart of accounts?
- What is the need of country chart of account or alternate chart of account? How country chart of account helps fulfill a business requirement?
- What is the need for group chart of account? How group chart of account helps in consolidation of financial data?
- What is non leading ledger in sap fico?
- What is company code global settings? What global parameter is assigned to company code?
- What is fiscal year variant? Why fiscal year variant is assigned to company code?
- What is posting period variant? Why posting period variant is assigned to company code?
- What is field status variant? What is field status group?
- What is document type in sap? Explain the purpose of document type?
- Document date vs Posting date vs Entry date vs Translation date. Explain
- What is posting key? what is the use of posting key?
- Document header & line items capture information of business transaction.
- Everything about currency & exchange rate in sap.
- Foreign currency valuation in sap. Explain with example
- Retained earnings account helps in year end balance carry forward. Explain
- What is the significance of tolerance groups in sap?
- What parameters are maintained in GL master and how does it impact in document posting?
ACCOUNTS PAYABLE
- What is meant by accounts payable in sap?
- Understanding procure to pay (PTP) cycle and accounting document at each step.
- Understanding MM FI integration in very simple terms.
- Purchase order price determination in SAP. Explained in very simple words.
- House bank, Bank key, Account ID in SAP
- What configuration (FBZP) needed for executing F110 in sap ?
ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE
- How sap overcomes challenges in accounts receivable process?
- What is customer reconciliation account?
- Understanding order to cash cycle in sap.
- Understanding SD FI integration in very simple terms.
- What is lock box? How lockbox helps in collection from customers?
TAX ACCOUNTING
- How sap helps in tax accounting?
- Tax configuration in sap: Tax procedure, Tax code & Tax jurisdiction code
- Concept of tax jurisdiction code & tax jurisdiction structure
- Significance of “Tax category & Posting without tax allowed” in GL master.
- Tax base amount and Discount base amount
- Assigning tax code V0 & A0 for non taxable transaction?
- Deductible input tax vs non deductible input tax
WITHHOLDING TAX
- Withholding tax in sap explained with example.
- How sap overcomes challenges in managing withholding tax?
- Withholding at the time of invoice or payment
- Withholding tax configuration in sap
- Business place & Section code in sap
- Withholding tax certificate numbering in sap
- Withholding tax report for filling tax returns
ASSET ACCOUNTING
- How sap helps in asset accounting?
- What is meant by asset accounting?
- What is the use of asset class?
- What is the use of depreciation key in asset accounting?
- Depreciation area and Chart of depreciation in sap.
- Derived depreciation area VS real depreciation area?
- Understanding asset accounting configuration needed in sap
- GL account determination for posting asset transaction
- Asset transaction and corresponding accounting document?
- How depreciation is posted in sap?
SAP CONTROLLING