Company needs to keep track of asset throughout the lifetime of asset. At any given point of time, company should know the entire history of asset starting from asset acquisition to asset retirement.
Whenever any transaction involving asset takes place, finance department has to update the account book by posting accounting document.
Below are few examples of asset transaction and corresponding accounting document:
→Asset acquisition from external vendor
Asset of 60000 is purchased from vendor. Asset has useful life of 5 years.
Finance department has to post below accounting document.

→Asset depreciation (if linear depreciation is applied then each month asset will be depreciated by 1000)
Each month finance department has to post below accounting document.

Depreciation will happen each month, hence accounting document for depreciation needs to be posted each month.
If at any point of time, company should be able to know net book value of the asset.
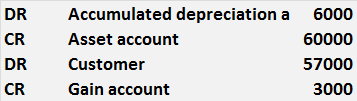
→Asset sale to customer
After 6 months, asset is sold to a customer for 57000
Finance department will need to post below accounting document.
Challenges in asset accounting:
- Keeping track of assets throughout the lifetime of asset: Since company has large number of asset, keeping track of each & every single asset is required but not possible manually.
- It is not possible to manually note down the accounting impact of each & every asset transaction. Hence generation of accounting document needs to be automated.
- Organization needs to prepare financial reports (balance sheet and profit & loss statement) using multiple accounting principles. In order to be able to produce financial reports in each accounting principle, every transaction of asset needs to be recorded in all accounting principles.
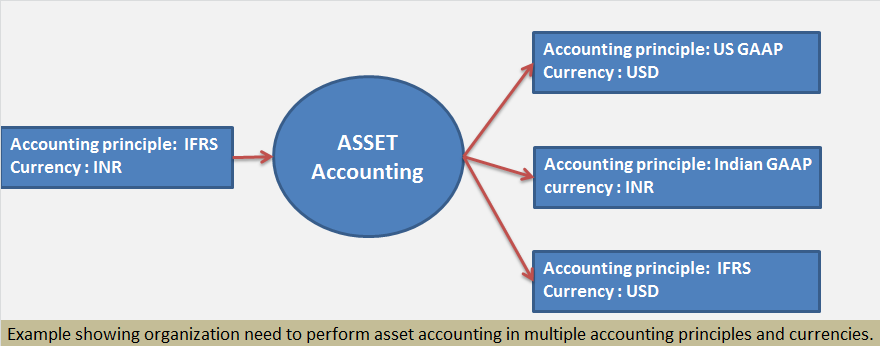
Consider below example:
Group Company is in USA and subsidiary company is in India.
Then company code in India might be required to perform asset accounting as per below:
Each accounting principle may recommend a different treatment of the asset transaction. For example:
- An accounting principle might recommend linear depreciation method while other may recommend non-linear depreciation of asset.
- Different accounting principles may recommend different useful life of the same asset.
Hence managing asset in multiple accounting principles and currencies increases complexity and becomes challenging.
How sap helps in overcoming challenges in asset accounting?
- Sap enables tracking of each & every asset over the entire lifetime of asset.
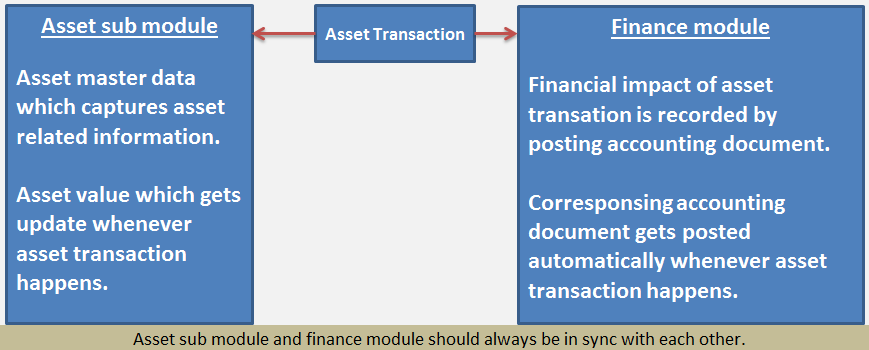
Asset accounting is a separate sub module in sap which comes under main module SAP FI.
Asset is tracked in asset sub module and corresponding financial impact is recorded in finance module.
For each & every asset, asset master is created in sub module which captures information related to the asset. Asset sub module also captures asset value which gets updated whenever any transaction of the asset happens.
- With the help of sap, accounting document gets generated automatically. Hence chance of any error due to manual intervention is greatly reduced.
- Sap makes it possible to manage asset in multiple accounting principle and currency.
With the help of sap, asset accounting can be performed in multiple accounting principles and currency.
GL ACCOUNTING
- What is SAP FICO ?What business requirement is fulfilled in this module?
- What is enterprise structure in sap fico?
- What is GL account? What is account group? What is operational chart of accounts?
- What is the need of country chart of account or alternate chart of account? How country chart of account helps fulfill a business requirement?
- What is the need for group chart of account? How group chart of account helps in consolidation of financial data?
- What is non leading ledger in sap fico?
- What is company code global settings? What global parameter is assigned to company code?
- What is fiscal year variant? Why fiscal year variant is assigned to company code?
- What is posting period variant? Why posting period variant is assigned to company code?
- What is field status variant? What is field status group?
- What is document type in sap? Explain the purpose of document type?
- Document date vs Posting date vs Entry date vs Translation date. Explain
- What is posting key? what is the use of posting key?
- Document header & line items capture information of business transaction.
- Everything about currency & exchange rate in sap.
- Foreign currency valuation in sap. Explain with example
- Retained earnings account helps in year end balance carry forward. Explain
- What is the significance of tolerance groups in sap?
- What parameters are maintained in GL master and how does it impact in document posting?
ACCOUNTS PAYABLE
- What is meant by accounts payable in sap?
- Understanding procure to pay (PTP) cycle and accounting document at each step.
- Understanding MM FI integration in very simple terms.
- Purchase order price determination in SAP. Explained in very simple words.
- House bank, Bank key, Account ID in SAP
- What configuration (FBZP) needed for executing F110 in sap ?
ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE
- How sap overcomes challenges in accounts receivable process?
- What is customer reconciliation account?
- Understanding order to cash cycle in sap.
- Understanding SD FI integration in very simple terms.
- What is lock box? How lockbox helps in collection from customers?
TAX ACCOUNTING
- How sap helps in tax accounting?
- Tax configuration in sap: Tax procedure, Tax code & Tax jurisdiction code
- Concept of tax jurisdiction code & tax jurisdiction structure
- Significance of “Tax category & Posting without tax allowed” in GL master.
- Tax base amount and Discount base amount
- Assigning tax code V0 & A0 for non taxable transaction?
- Deductible input tax vs non deductible input tax
WITHHOLDING TAX
- Withholding tax in sap explained with example.
- How sap overcomes challenges in managing withholding tax?
- Withholding at the time of invoice or payment
- Withholding tax configuration in sap
- Business place & Section code in sap
- Withholding tax certificate numbering in sap
- Withholding tax report for filling tax returns
ASSET ACCOUNTING
- How sap helps in asset accounting?
- What is meant by asset accounting?
- What is the use of asset class?
- What is the use of depreciation key in asset accounting?
- Depreciation area and Chart of depreciation in sap.
- Derived depreciation area VS real depreciation area?
- Understanding asset accounting configuration needed in sap
- GL account determination for posting asset transaction
- Asset transaction and corresponding accounting document?
- How depreciation is posted in sap?
SAP CONTROLLING